The start of 2026 has brought a mix of growth, risk, and experimentation across crypto and AI.
Stablecoins are leading protocol revenues, while a major smart contract exploit affected Matcha Meta users. Colombian investors will soon have limited access to a Bitcoin-linked pension fund, and security researchers are warning about exposed data in the viral AI assistant Clawdbot.
This digest reviews four stories that show how market trends, regulation, and cybersecurity are changing digital finance and future technologies.
Top gainer and loser coins for the week first.
Top gainers and losers
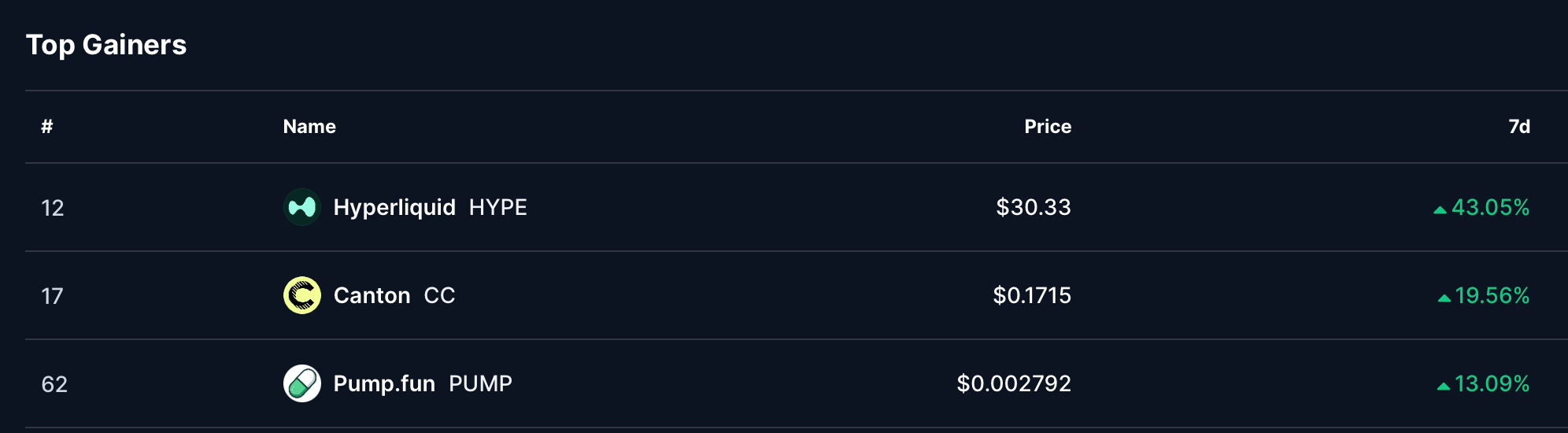
- Hyperliquid (HYPE) - Impressive rise of 43.05% this week up to a price of $30.33
- Canton (CC) - 19.56 growth to a week price of $0.1715
- Pump.fun (PUMP) - closing this week with a price of $0.002792 and growth of 13.09%
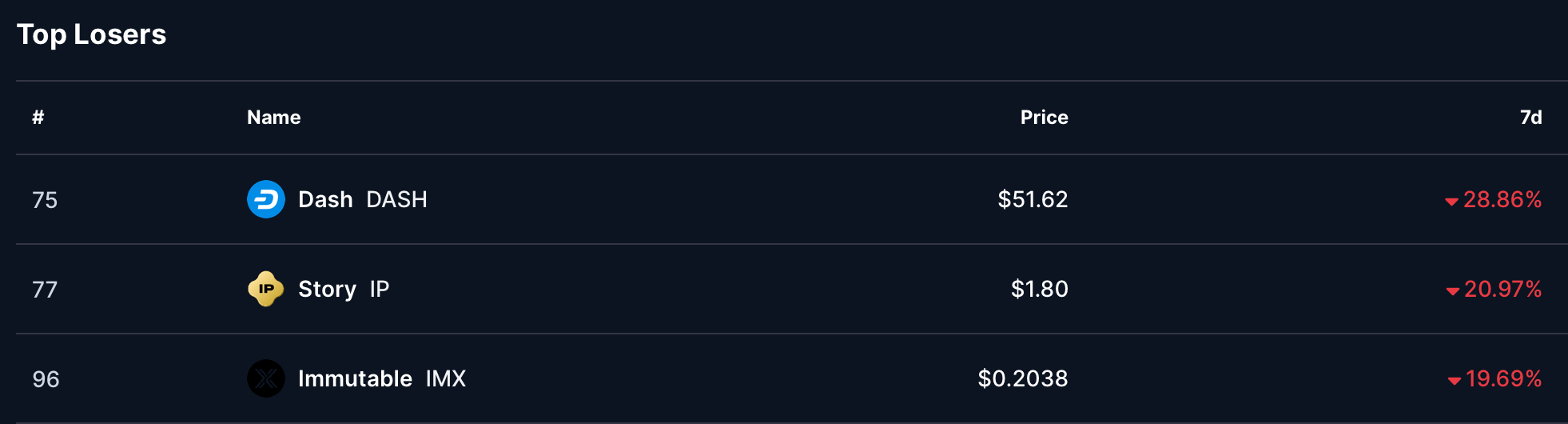
- Dash (DASH) - 28.86% drop to a price of $51.62
- Story (IP) - end week price of $1.80 and weekly drop of 20.97%
- Immutable (IMX) - 19.69% drop this week to a price of $0.2038
Stablecoins dominate crypto revenue as Tether leads protocols in 2025
Tether generated the highest protocol revenue based on calendar-year 2025 data, according to CoinGecko Research, reinforcing the growing role of stablecoins as core infrastructure rather than ancillary tools. CoinGecko’s 2025 Annual Crypto Industry Report estimates Tether produced approximately $5.2 billion in revenue, representing 41.9% of total revenue across 168 tracked crypto protocols.
Revenue concentration among stablecoin issuers was substantial. Tether, Circle, Ethena, and MoonTrade together generated about $8.3 billion, accounting for 65.7% of all recorded protocol revenue.
The distribution reflects where usage persisted during weaker market conditions: dollar-denominated liquidity, settlement rails, and reserve-backed issuance continued to attract demand even as speculative activity slowed.
INSIGHT: Stablecoins generated $5.2B in revenue in 2025, accounting for 41.9% of total protocol revenue. pic.twitter.com/fjJrAn9k7B
— CoinGecko (@coingecko) January 25, 2026
Stablecoin supply growth supported this outcome.
Total stablecoin market capitalization increased 48.9% over the year, expanding by $102.1 billion to reach $311.0 billion. Larger circulating balances translated into consistent issuer revenue tied to transaction activity and interest-bearing reserves, largely independent of crypto asset price movements.
Among blockchains, Tron ranked second with an estimated $3.5 billion in revenue. CoinGecko attributes this performance to Tron’s position as the primary network for USDT transfers. Low transaction costs and high throughput made it a preferred settlement layer, allowing the network to capture value through transaction volume rather than application-level activity.
Trading platforms filled out most of the remaining top ten but showed far greater earnings volatility. Phantom’s revenue offers a clear example: the wallet generated $35.2 million in January during heightened meme coin activity on Solana, then declined to $8.5 million by December as speculative interest faded. Similar revenue compression followed October’s $19 billion liquidation event, after which trading volumes became increasingly driven by forced activity rather than discretionary risk-taking.
At the aggregate level, monthly protocol revenue remained relatively stable, fluctuating between roughly $3 billion and $3.5 billion for much of the year. That stability reflected offsetting trends within the sector, as declining trading income was balanced by steady payments and settlement usage.
The broader market backdrop remained challenging.
Total crypto market capitalization closed the year at $3.0 trillion, down 10.4% year over year, the first annual decline since 2022. Within that environment, stablecoin-linked protocols captured a growing share of total economic output, while trading platforms remained closely tied to market cycles.
Matcha Meta users affected by $13.4 million SwapNet smart contract exploit
A limited number of Matcha Meta users were impacted by a smart contract exploit involving SwapNet, after attackers drained approximately $13.4 million in crypto from contracts that had been explicitly approved by users. Matcha Meta disclosed the details in a post-mortem published this week, confirming the vulnerability originated within SwapNet’s own smart contracts.
According to the report, confirmed losses affected 20 users who had manually disabled Matcha Meta’s default One-Time Approval setting and instead granted direct token allowances to SwapNet contracts. Users who retained the One-Time Approval feature, which routes transactions through 0x’s AllowanceHolder contract, were not exposed to the exploit.
Matcha Meta said the incident stemmed from flaws in SwapNet’s contract design rather than any issue within Matcha Meta’s routing infrastructure or the 0x protocol. Following a joint review with the 0x team, the company confirmed that AllowanceHolder and Settler contracts were not involved and remain secure.
Initial estimates of the exploit’s scope varied among blockchain security firms. CertiK reported losses of approximately $13.3 million and attributed the incident to an arbitrary call vulnerability that enabled unauthorized transfers from approved contracts.
PeckShield issued a higher preliminary estimate of up to $16.8 million, though Matcha Meta later clarified that this figure included a separate and unrelated $3.4 million incident tied to Aperture Finance.
Based on its internal investigation, Matcha Meta placed confirmed losses from the SwapNet exploit at $13.43 million. Onchain data showed that a single user accounted for roughly $13.34 million of the total. The attacker swapped assets on Base before bridging funds to Ethereum.
SwapNet paused its Base contracts roughly 45 minutes after the initial exploit, with deployments on other networks disabled soon after. Matcha Meta said it has since removed SwapNet from its aggregator, permanently disabled the ability for users to opt out of One-Time Approval, and added safeguards aimed at preventing similar exposure.
The incident adds to a broader pattern of persistent security losses across the crypto sector. Blockchain analytics firm Chainalysis estimates that cryptocurrency theft exceeded $3.41 billion during 2025, slightly higher than the prior year. A single $1.5 billion breach at Bybit accounted for 44% of total losses, while North Korea-linked actors were responsible for a record $2.02 billion stolen over the year.
Colombia’s second-largest pension fund prepares limited Bitcoin exposure for qualified clients
AFP Protección, Colombia’s second-largest private pension and severance fund manager, is preparing to launch an investment product with exposure to Bitcoin. The move places Protección among a small group of pension administrators in the country offering regulated access to digital assets.
Juan David Correa, president of Protección SA, confirmed the initiative in an interview with local outlet Valora Analitik. Access to the Bitcoin-linked fund will be restricted to qualified investors and offered through a personalized advisory process designed to assess suitability and risk tolerance. Participation will be optional, and allocations will be limited to a defined portion of eligible portfolios.
Correa said the initiative is intended to provide diversification rather than alter portfolio construction. Clients who qualify will be able to add Bitcoin exposure if they choose, while maintaining existing investment structures.
“The most important element is diversification,” Correa added
Protección said the product does not represent a change in how Colombian pension savings are managed. Fixed income instruments, equities, and other traditional assets will remain the core of pension portfolios. The Bitcoin-linked fund is structured as an additional option for clients who meet eligibility requirements.

Founded in 1991, AFP Protección manages more than 220 trillion Colombian pesos, or approximately $55 billion, for over 8.5 million clients across mandatory and voluntary pension plans and severance accounts. Its entry follows a similar decision by Skandia Administradora de Fondos de Pensiones y Cesantías, which introduced Bitcoin exposure in one of its portfolios in September last year. Protección becomes the second major pension fund administrator in Colombia to offer this type of product.
Colombia’s mandatory pension fund system held 527.3 trillion pesos in assets as of November 2025. Nearly half of those assets were invested abroad. Digital asset exposure remains limited within the system under current allocation frameworks.
The launch coincides with tighter oversight of the crypto sector. Earlier this month, Colombia’s tax authority, DIAN, implemented mandatory reporting rules for crypto service providers. The framework aligns with the OECD’s Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework and requires exchanges, custodians, and intermediaries to collect and submit user and transaction data. Penalties apply for noncompliance.
Viral AI assistant ‘Clawdbot’ risks exposing private messages and credentials
Cybersecurity researchers have warned that the AI assistant Clawdbot could expose private chats, API keys, and credentials due to misconfigured servers. The warnings follow Clawdbot’s surge in popularity over the past weekend, according to Mashable.
Blockchain security firm SlowMist identified a “gateway exposure” affecting Clawdbot, putting “hundreds of API keys and private chat logs at risk.”
The firm said, “Multiple unauthenticated instances are publicly accessible, and several code flaws may lead to credential theft and even remote code execution.”

Researcher Jamieson O'Reilly reported that “hundreds of people have set up their Clawdbot control servers exposed to the public” over recent days.
The vulnerability occurs when the Clawdbot gateway is deployed behind an unconfigured reverse proxy, allowing unauthorized users to locate servers using basic internet searches.
“Searching for ‘Clawdbot Control’ — the query took seconds. I got back hundreds of hits based on multiple tools,” O'Reilly said.
Exposed servers could reveal API keys, bot tokens, OAuth secrets, signing keys, and full conversation histories across messaging platforms. Attackers could also send messages as the user and execute commands remotely.
“If you’re running agent infrastructure, audit your configuration today. Check what’s actually exposed to the internet. Understand what you're trusting with that deployment and what you're trading away,” O’Reilly advised.
Clawdbot differs from other AI assistants because it runs locally with full system access, allowing it to read and write files, execute scripts, control browsers, and run commands. Matvey Kukuy, CEO of Archestra AI, demonstrated the risk by extracting a private key from a test machine in five minutes using prompt-injection techniques.
The Clawdbot FAQ highlights the risks, stating:
“Running an AI agent with shell access on your machine is… spicy. There is no ‘perfectly secure’ setup.”
It adds that malicious actors could “try to trick your AI into doing bad things, social engineer access to your data, and probe for infrastructure details.”
To reduce risk, SlowMist recommends strict IP whitelisting on exposed ports and careful configuration of control servers.

Disclaimer: All materials on this site are for informational purposes only. None of the material should be interpreted as investment advice. Please note that despite the nature of much of the material created and hosted on this website, HODL FM is not a financial reference resource, and the opinions of authors and other contributors are their own and should not be taken as financial advice. If you require advice, HODL FM strongly recommends contacting a qualified industry professional.




